Software Architecture: The Implementation View
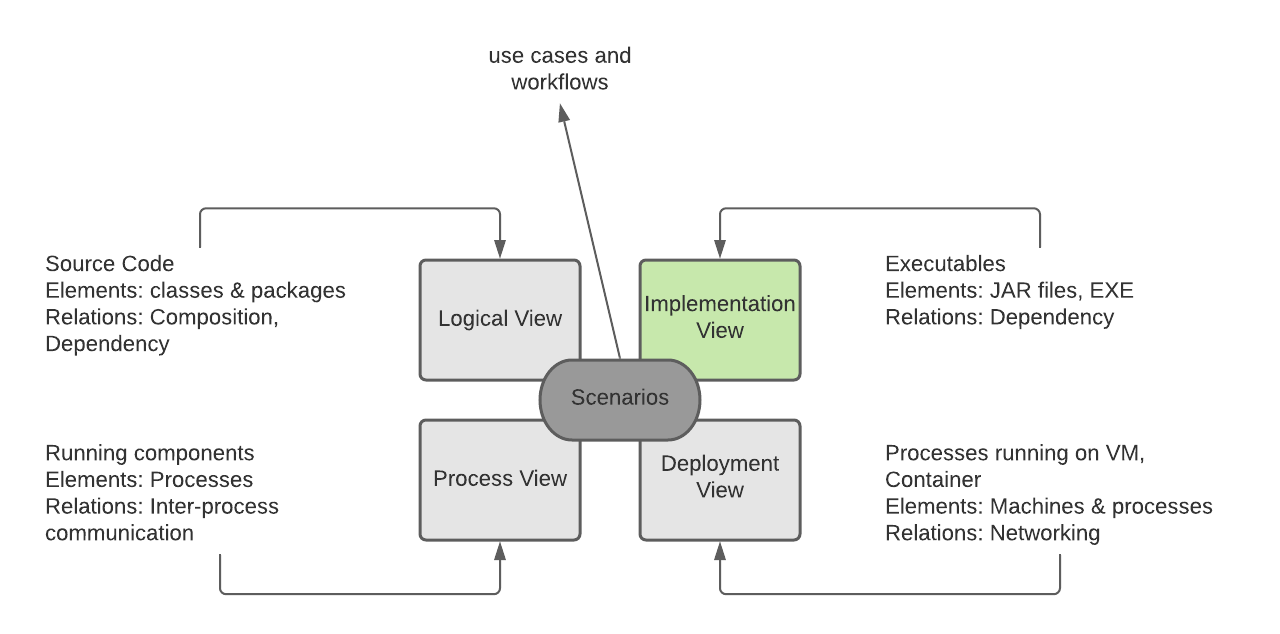 The 4+1 view model describes an application’s architecture using four views, along with scenarios that show how the elements within each view collaborate to handle requests
The 4+1 view model describes an application’s architecture using four views, along with scenarios that show how the elements within each view collaborate to handle requests
Includes the result of the build process that can be run or deployed such as a Java JAR or Node.js Package. These artifacts interact with each other in the form of a composition or dependency relationship.
The Monolithic Architecture Style
Let's extract the definition of monolithic architecture from an example. Imagine you are invited to develop an enterprise application for
managing music concerts ticketing, One of the requirements is to access the system from the browser and a mobile native application. SO the application
will handle HTTP requests, execute a function and access a database to persist the data. One of the design options we may have
is to create different components each one is responsible for a specific business logic (event subscription, payments, ticket editing ...). if we choose to develop with
the java programming language and the spring framework, we'll have one application with many modules interconnected and coupled to accomplish
the job. But what about the deployment? what type of build output will generate and how to deploy it into a production environment.
The answer is we will generate a single Java WAR file.
The monolithic representation of our example application (Music Event Application) where we can distinguish bounded functions of the system but all in one artifact
This is what monolithic architecture is about to define the output of your source code as one piece that you can easily:
- Deploy (push or put into the production environment, or any other environment such as development or staging)
- Scale (run multiple instances of the application in response to increasing traffic)
- Debug (in case of non-normal behavior of the system you can explore the logs, check the config, and so on to find the error, all these things are on the same process)
- Question: Now the system is up and running, but a new feature is required which needs to update the payment provider within our application, how can we achieve that?
- Answer: we have to update the source code, re-build the whole application, think of a deployment strategy to ensure service continuity of our application.
In the context of our monolithic application, many drawbacks are rising while changing a small piece of the system:
- Even though the change concern only one part of the system, this one becomes indivisible and decoupled, the build and deploy process is slower because all the source code should be re-build to generate the new artifact (Java WAR file)
- The whole system is developed with one stack which limits the on-boarding of other developers with different backgrounds
- Less re-usability of the components.
- Increasing the artifact (build output) volume.
- Reliability as one bug in the ticket editing component can cause the whole system to shut down.
In the next section, we discuss the alternative and how microservices address many of the drawbacks of monolithic and bring new added value but also some very challenging points to handle.
The Microservices Architecture Style
Microservices architecture style organizes the application as a set of loosely coupled, independently deployable services, Together these services deliver the functional and business features of the system we want to build. Let's continue with our Music Event Application example and try in the above illustration to define its microservices architecture:
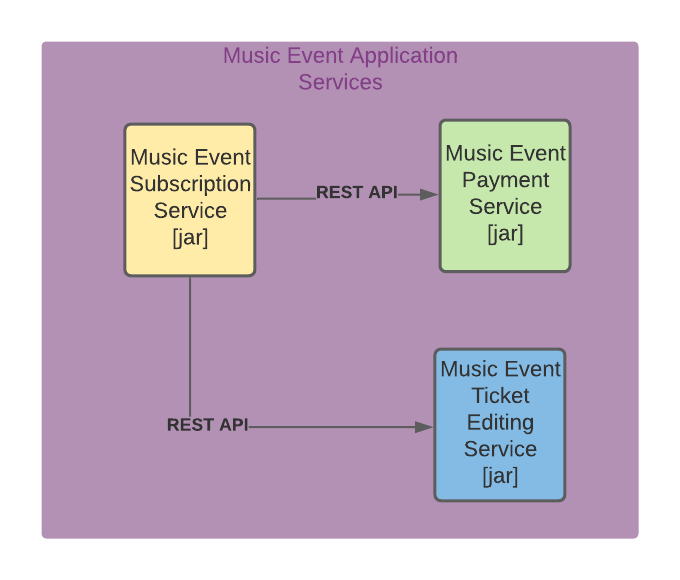 The Microservices representation of our example application (Music Event Application) where 3 services communicate through HTTP using REST
The Microservices representation of our example application (Music Event Application) where 3 services communicate through HTTP using REST
As we can observe in the illustration each service run in an independent process and also could have its database(recommended), Notice also how these services communicate to each other, in this example, I suggest using the REST API through HTTP, but this is not the only communication option we can have, there are more such as messaging using a message broker.
Let's tackle with further detail the microservices inter-communications in a dedicated article, so far and the rest of this document we will use REST as a reference.
What is a service?
As the word service is a most recurrent when we explore the microservice architecture, Here is a definition:
A service is an independent deployable application or software component that provides a set of functionalities accessible through an API. Service has its own logical architecture, Hexagonal architecture may fit many use-cases, In addition a service can be developed with its specific technology stack that may differ from other services' technology stacks in a microservices architecture
read more about Hexagonal Architecture and alternatives in this article
What is loosely coupled Services and why they should?
Two services are loosely coupled if changes in the design, implementation, or behavior in one won't cause change in others. In a Microservices architecture, the coupling will happen when a change in one enforces an almost immediate change to one or more microservices that collaborate with it directly or indirectly.
While designing Microservices architecture, to make the services the less coupling possible, consider the following points:
Database sharing
the data storage is a microservice implementation detail that should be hidden from its clients (usually other microservices). If Microservice A needs to access data of Microservice B, B should provide an API that A will use to consume the needed data
Code Sharing
By definition, microservices do not share codebase, but we may want to avoid redundancy by sharing dependency libraries and end up needing to update frequently in response to that libraries' client's change requests. So shared code should be as minimum as possible. A good practice that may seem strange at glance is to duplicate code so each service has its copy, so we need to update the library to match Service A requirements, Service B remains un-impacted
Synchronous Communication
In a Microservice architecture, services cooperate to accomplish the job, so they need to communicate either asynchronously or synchronously where the service caller expects a timely response from the callee service might even block while it waits. To address the potential response latency, we can integrate a caching mechanism or implement the circuit breaker pattern to avoid cascading failures. These two options could help remediate the system quickly, but for the long term, the best alternative is switching to asynchronous communication by using a messaging broker like Apache Kafka, So services can cooperate by publishing and consuming messages.
When it comes to designing the next-generation software, relying on a strong and reliable architecture helps a lot, In recent decades, much great software conquered the market and is serving millions of users while scaling up and down to reduce cost and energy or respond to an increasing number of requests. Microservices Architecture is part of other practices and engineering designs behind thanks to its benefits, below is a non-exhaustive list:
- Independent development: microservices can be developed in isolation to accomplish a defined functionality
- Independent deployment: microservices can be deployed individually and independently in any environment (cloud, on-premise, managed infrastructure)
- Fault isolation: if one service fails, the system remains up and only the functionality provided by that stopped microservice will be impacted
- Technology stack: different programming languages, frameworks, and technologies can be used to build the same software, usually a SaaS
- Individually scaling: each service can scale as per need, is not necessarily to scale the whole system as is the case of monolithic based application
Despite the number of advantages Microservices Architecture is bringing, choosing it over Monolithic Architecture relies upon on the context, the application domain (banking, delivery, e-commerce, ...) and scope (either is a lightweight application or a complex evolving application), your organization software engineering capabilities and culture.


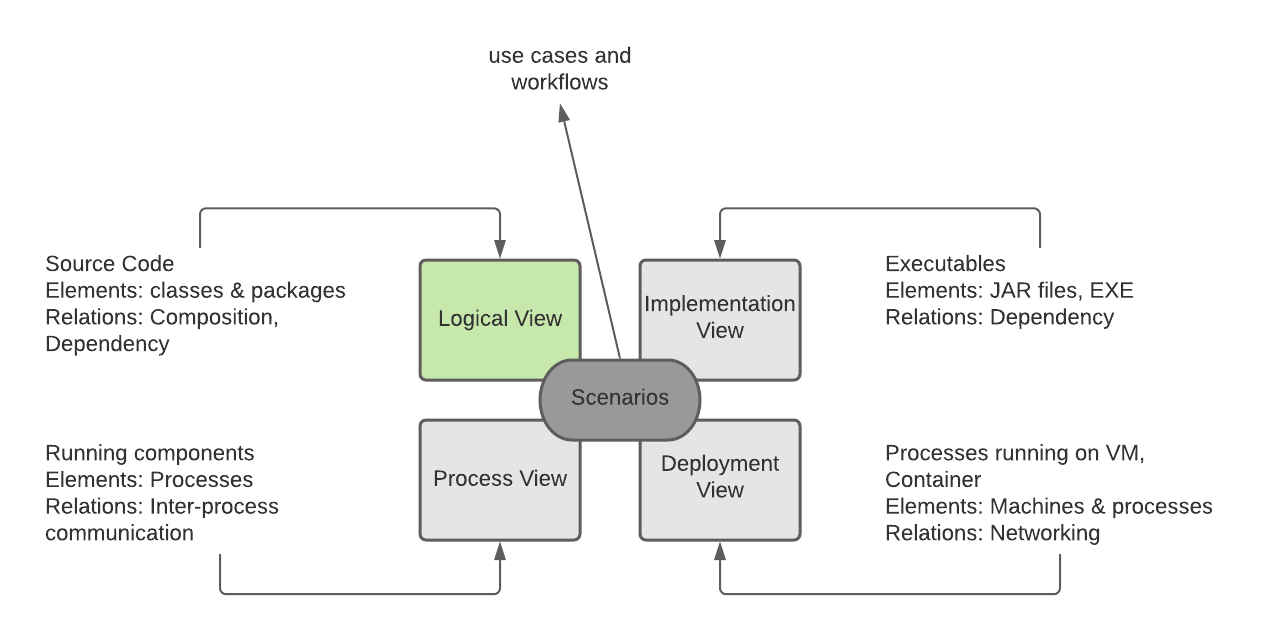 The 4+1 view model describes an application’s architecture using four views, along with scenarios that show how the elements within each view collaborate to handle requests
The 4+1 view model describes an application’s architecture using four views, along with scenarios that show how the elements within each view collaborate to handle requests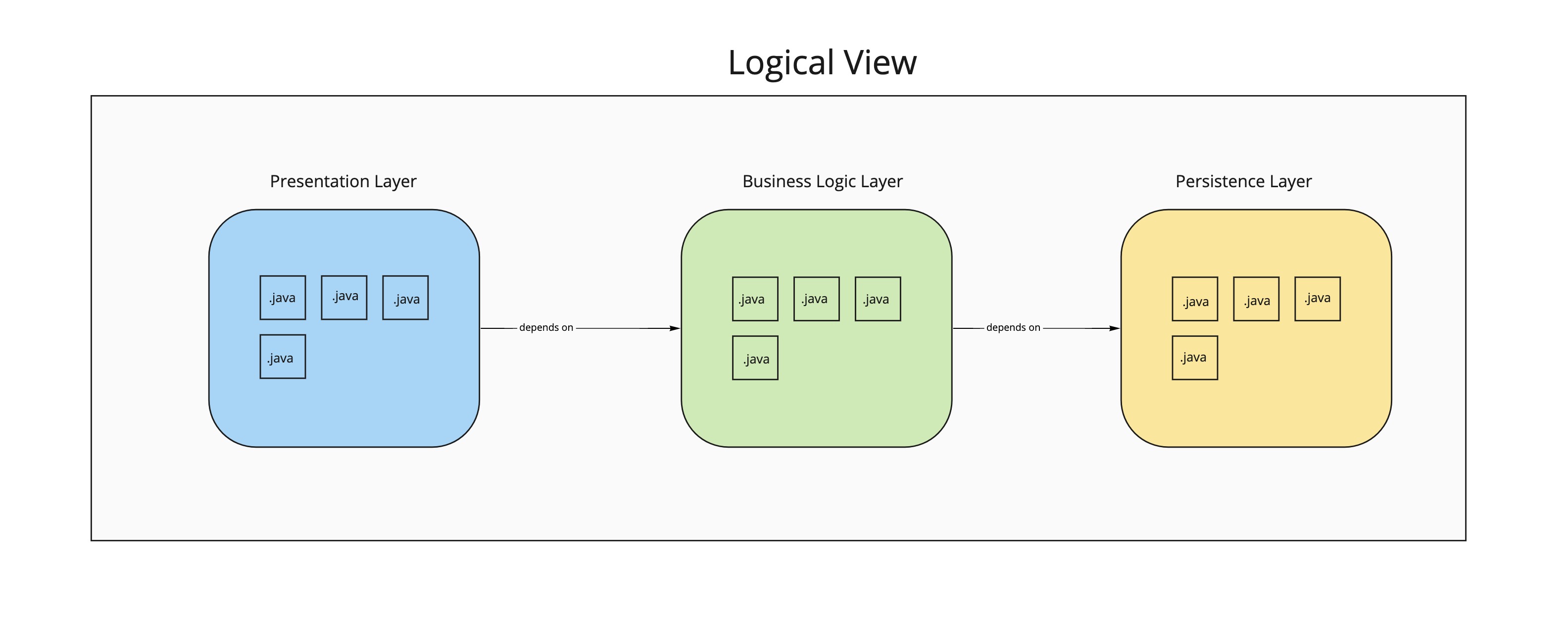 In the above figure, we illustrate the 3 tier architecture for a java application, classes of the same layer are grouped using packages.Note that architecture is beyond
any programming language, so for example in case of a C# application we group classes in namespaces instead of packages for java.
In the above figure, we illustrate the 3 tier architecture for a java application, classes of the same layer are grouped using packages.Note that architecture is beyond
any programming language, so for example in case of a C# application we group classes in namespaces instead of packages for java.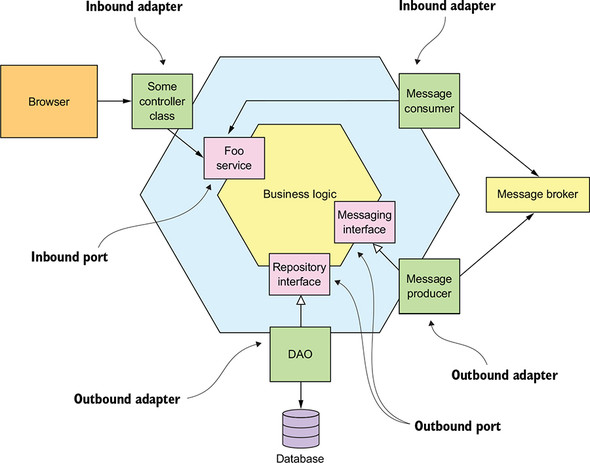

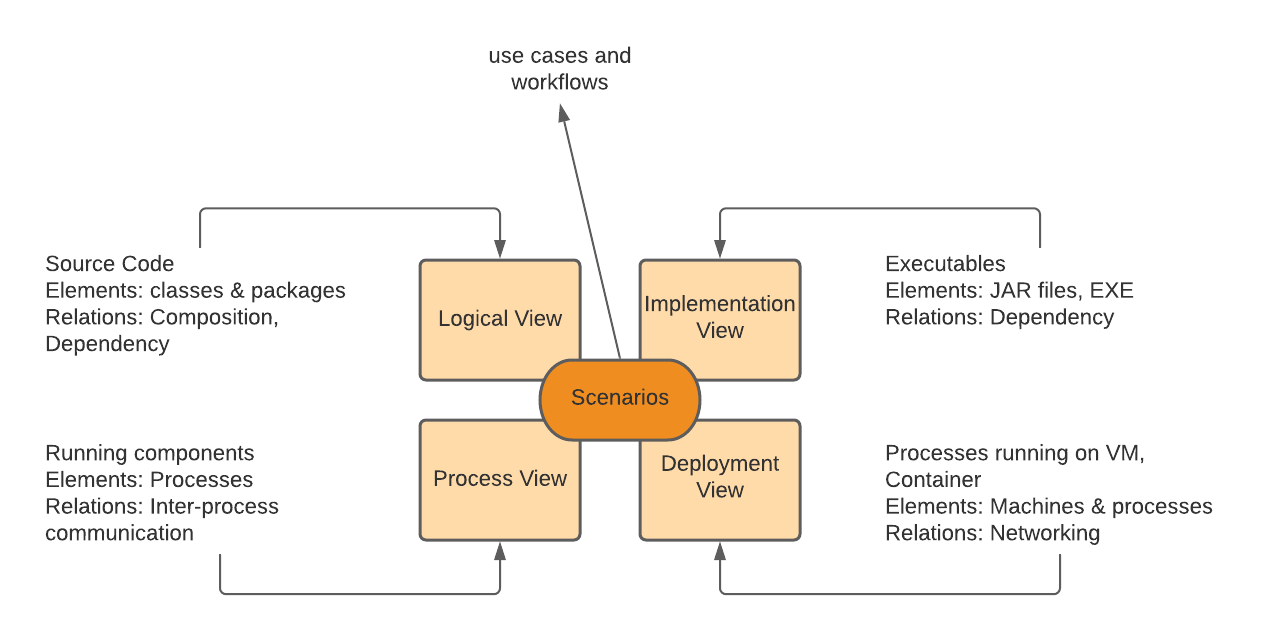 The 4+1 view model describes an application’s architecture using four views, along with scenarios that show how the elements within each view collaborate to handle requests
The 4+1 view model describes an application’s architecture using four views, along with scenarios that show how the elements within each view collaborate to handle requests